Chapter 6 Reading Guide the Human Population and Its Impact
Chapter 10 ~ Global Populations
Key Concepts
- Outline the process of cultural evolution and explain how it has increased the carrying capacity for the human population.
- Describe the growth of the human population during the past 10,000 years.
- Explain why population growth has been especially rapid during the past several centuries.
- Discuss why there are large differences in population growth rates between developed and less-developed countries.
- Explain the demographic transition and how it affects age-class structure and population growth.
- List the major methods of birth control, and discuss why they are controversial.
- Explain what a population policy is, and how it can affect future human population.
- Outline possible causes of a population crash.
- the population growth has been sustained over a long period of time
- an extraordinarily large abundance has already been achieved
- there has been a similarly impressive population growth of species that live in a close, mutualist relationship with humans, such as cows, pigs, chickens, and agricultural plants, which have their own cumulative environmental impacts
- a remarkable variety of species and ecosystems is being exploited as natural resources to support the human enterprise
Cultural Evolution and Carrying Capacity
- the invention and improvement of tools and weapons
- discoveries of edible and medicinal species
- the elaboration of language and other means of communication
- the development of improved social organizations
- the mastery of fire
- the domestication of the dog, which allowed hunting to be more efficient, provided a pack animal, and helped keep encampments clean
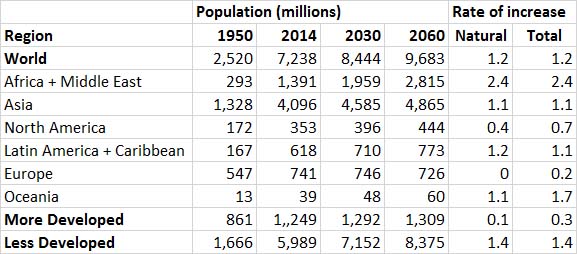
Populations of Particular Countries
Birth and Death Rates
- the use of traditional medicines to prevent conception or to induce abortion
- infibulation, or the insertion of pebbles or other objects into the uterus, where they may be retained for years, and prevent the implantation of fertilized ova
- the use of mechanical means of inducing abortion
- infanticide, or the killing of newborn infants
- use of means to raise the temperature within the scrotum, such as wearing a warming pouch, which inhibits sperm production and reduces fertility of the male
Less-Developed Countries
Developed Countries
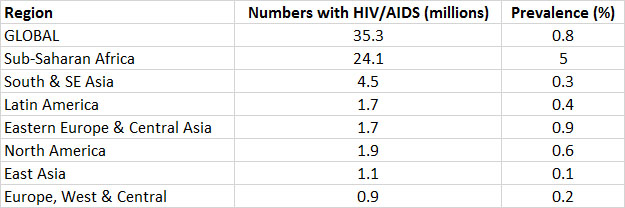
A Pandemic
Famine
- the population is large and dense
- there are only small reserves of stored food
- the environmental conditions for agriculture are marginal, partly because population pressure has led to land being cultivated in semi-arid regions that are susceptible to drought
- there is little foreign exchange to purchase food from elsewhere during times of shortage, so people and governments must rely on goodwill and aid
- the economic and political systems do not foster the stable governments and social systems that are required for effectively dealing with crisis
- encouraging immigration (which has more than double the influence on population growth in Canada than does natural increase; see Chapter 11)
- in particular, encouraging the immigration of younger persons, who have a relatively long lifespan within the working economy and so would help to offset the increased "aging" of the general population
- having more babies – various jurisdictions have enacted pro-natalist policies to encourage larger family sizes, such as financial subsidies and relief from income tax
- ensuring that Canadians have easy access to safe and effective measures of birth control, which allows people to make choices about their reproduction and family size
Decline of Carrying Capacity
A Nuclear Holocaust
A Natural Big Bang
- What are major stages of cultural evolution? How do they relate to changes in carrying capacity and growth of the human population?
- Explain the demographic transition. Compare its dynamics in developed and less-developed countries.
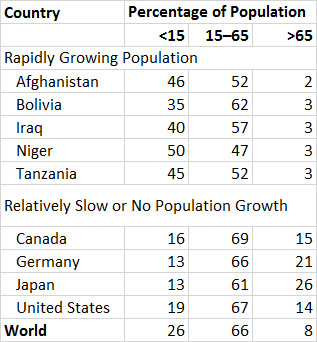
- Why is age-class structure so important in future growth of a population?
- Describe possible reasons why the human population will eventually level off or decrease.
- What is the recent pattern of growth of the human population? Discuss possible scenarios for future growth.
- Compare demographic parameters and population growth rates in developed and less-developed countries. What social and economic factors explain the differences?
- What are the major means of birth control? Discuss controversies associated with their use.
- What is the likelihood of a human population crash? What are the potential causes?
- Why is HIV/AIDS more prevalent in poorer countries than in wealthier ones?
- The government of a less-developed country has asked for your help in designing a population policy. You will visit the country for several months to get an appreciation of the socio-economic and environmental problems that exist and to help you understand cultural influences on the design of a population policy. What kinds of studies would you want to make during your visit? What key elements would you recommend for the population policy?
- The personal choice to use birth control can be difficult and is further complicated by considerations about the various methods that are available. Make a list of the key ethical, social, and economic issues associated with any three methods of birth control (you can select them from In Detail 10.1). Consider both the personal dimensions of choice (personal ethics and views) as well as those relevant to society at large (such as group pressure, whether a particular method is legal, and the ease of access to particular methods).
References Cited and Further Reading
Chapter 6 Reading Guide the Human Population and Its Impact
Source: https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/environmentalscience/chapter/chapter-10-global-populations/
0 Response to "Chapter 6 Reading Guide the Human Population and Its Impact"
Post a Comment